

Alveolar ventilation (V A) was also calculated.Įighty-one infants with a median (range) gestational age of 28.7 (22.4-41.9) weeks were recruited. Volumetric capnograms were constructed to calculate the dead space using the modified Bohr-Enghoff equation. Expiratory tidal volume and carbon dioxide levels were measured. We determined if there were differences in dead space and alveolar ventilation in ventilated infants with pulmonary disease or no respiratory morbidity.Ī prospective study of mechanically ventilated infants was undertaken.
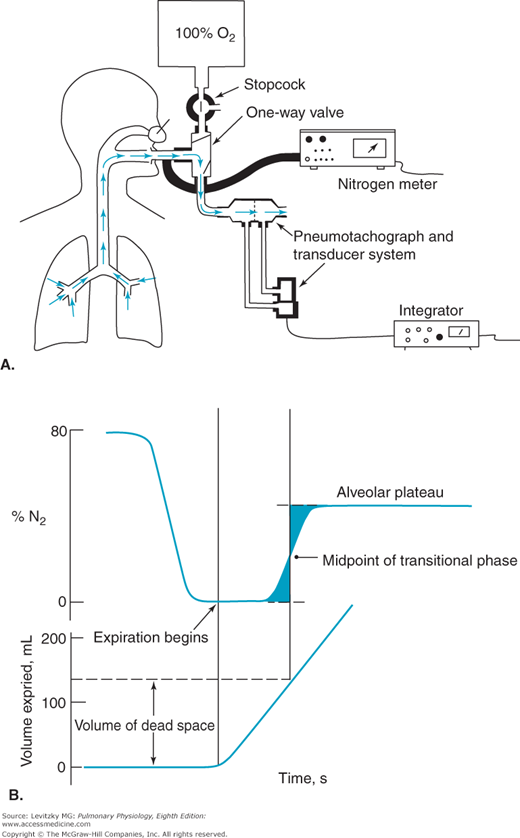
Dead space is the volume not taking part in gas exchange and, if increased, could affect alveolar ventilation if there is too low a delivered volume.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
